
高效储能材料与技术团队在氯离子电池领域取得重要进展。团队硕士研究生李西文(导师:隋艳伟教授、尹青副教授)以第一作者身份在国际顶级期刊《Advanced Energy Materials》发表题为Atomic Interface Engineering of NiFe-LDH@MXene via Halide Ions for High-Rate Chloride-Ion Batteries的学术论文。该研究通过阴离子介导的原子界面工程,协同优化了层状双金属氢氧化物(LDHs)电极材料的电子传导性与离子传输动力学,为高性能阴离子电池设计提供了新思路。
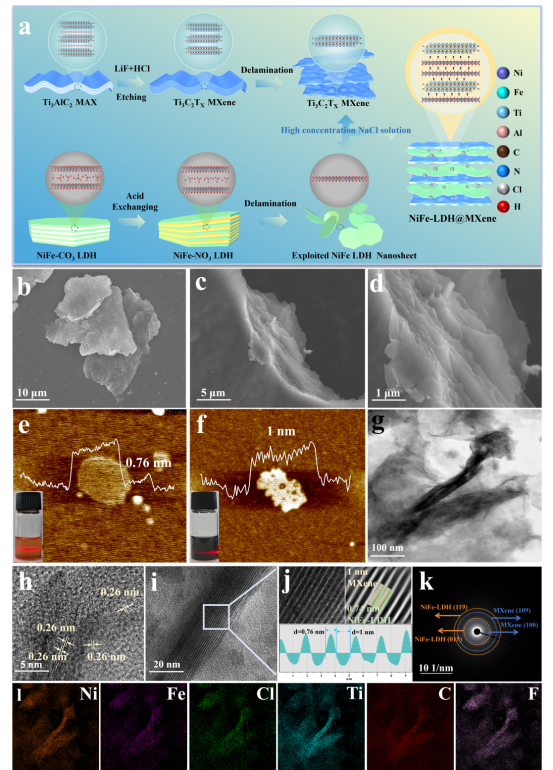
Figure. (a) Illustration for the synthesis process of the NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure. (b-d) SEM images of NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure. AFM images and height profiles of (e) NiFe LDH and (f) MXene. (g) TEM image of NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure. (h) TEM image, (i) HRTEM image, (j) FFT images and (k) SAED pattern image of NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure. (l) EDS mapping of NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure (Ni, Fe, Cl, Ti, C, F).
核心创新:氯离子桥接双通道异质结构
针对LDHs材料固有的低电导率与缓慢层间传输问题,研究团队提出空间电荷异质结构策略:
• 创新设计:利用带正电的NiFe-LDH纳米片与带负电的MXene层静电自组装,通过Cl⁻离子作为桥梁构建内置电场。
• 双通道协同:解耦MXene电子高速通道与LDH离子存储通道,显著提升氯吸附能力。
• 性能突破:优化后的1NiFe-LDH@2MXene正极在1000 mA g⁻¹高电流密度下循环1000次后,仍保持119.1 mAh g⁻¹可逆容量,单圈容量衰减率低至0.034%,体积应变仅2.4%。
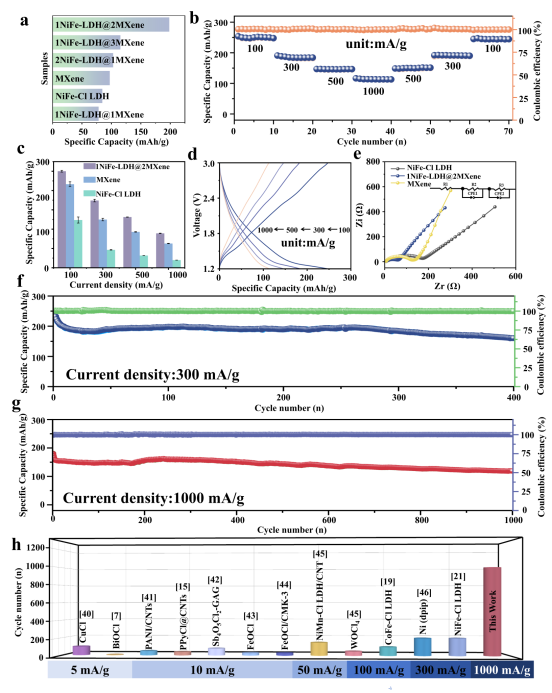
Figure. (a) Long-term cycling tests at 300 mAg−1 of NiFe-Cl LDH, MXene and NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructures. (b) Rate performance of 1NiFe-LDH@2MXene heterostructure. (c) Rate performance comparison of NiFe-Cl LDH, MXene and 1NiFe-LDH@2MXene heterostructure. (d) Charge/discharge curves at different current densities of 1NiFe-LDH@2MXene heterostructure. (e) Nyquist plots of NiFe-Cl LDH, MXene and 1NiFe-LDH@2MXene heterostructure. (f) Long-term cycling tests at 300 mA g−1 and (g) Long-term cycling tests at 1000 mAg−1 of 1NiFe-LDH@2MXene heterostructure. (h) Comparison of the long cycling life among 1NiFe-LDH@2MXene heterostructure and reported cathodes in CIBs.
机制解密:三重协同效应
综合表征与理论计算揭示性能提升机制:
• 拓扑限域:LDH层间结构定向引导晶格氧化还原反应。
• 界面赝电容:MXene导电网络与弗伦克尔缺陷界面协同加速电荷捕获。
• 动力学优化:面对面异质界面将有效扩散路径最小化,Cl⁻扩散能垒降至0.956 eV(较原始LDH降低35%)。
第一性原理计算证实:界面电荷离域使材料功函数从9.423 eV降至5.433 eV,显著降低肖特基势垒。
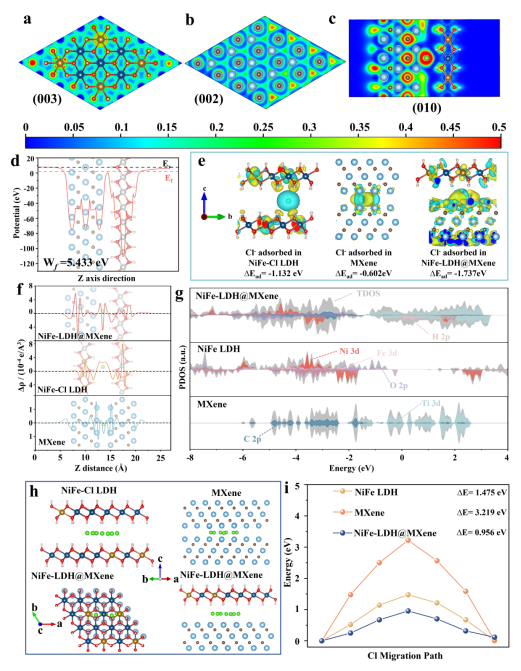
Figure. ELF 2D cross-section view of the (a) NiFe-Cl LDH, (b) MXene and (c) NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure. (d) Average potential profile along Z-axis direction for NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure. (e) Differential charge density distribution in the heterostructure interface of NiFe-Cl LDH, MXene and NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure. Cyan and Yellow area represent the electron depletion and accumulation, respectively. (f) The Charge density distribution of NiFe-Cl LDH, MXene, and the NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure along the Z direction. (g) DOS of NiFe-LDH, MXene and NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure. (h) Schematic depiction of the diffusion pathways of Cl− in NiFe-Cl LDH, MXene and NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure. (i) Schematic depiction of the diffusion barriers of Cl− in NiFe-Cl LDH, MXene and NiFe-LDH@MXene heterostructure.
普适性验证:多阴离子存储体系通用平台
研究进一步拓展至氟/溴离子电池体系:
• 氟插层类似物(NiFe-F LDH@MXene)与溴插层类似物(NiFe-Br LDH@MXene)
• 均保持明确的多级结构及稳定阴离子存储性能
验证了该异质界面设计策略在多元阴离子储能体系中的广泛适用性。
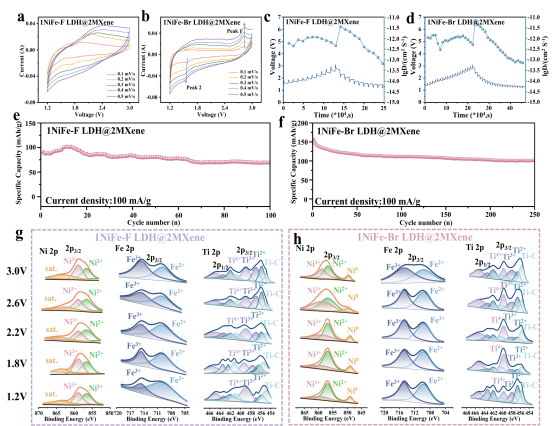
Figure. CV curves at different scan rates of (a) 1NiFe-F LDH@2MXene and (b) 1NiFe-Br LDH@2MXene heterostructures. GITT curve and chloride ion diffusion coefficient (DCl−) of (c) 1NiFe-F LDH@2MXene and (d) 1NiFe-Br LDH@2MXene heterostructures. Long-term cycling tests at 100 mA g−1 of (e) 1NiFe-F LDH@2MXene and (f) 1NiFe-Br LDH@2MXene heterostructures. Ex-situ XPS of (g) 1NiFe-F LDH@2MXene and (h) 1NiFe-Br LDH@2MXene heterostructures (Ni, Fe ,Ti).
结论指出:
本研究通过合理设计的界面电荷调控,解决了传统LDH体系中长期存在的电子-离子传输失配问题,为阴离子宿主电极工程化建立了合成指导原则。所提出的适配性方法学可扩展至其他多价电池体系,推动下一代高性能储能器件发展。
【团队导师简介】

隋艳伟
教授/博士生导师
中共党员,教授、博士生导师。2009年于哈尔滨工业大学获得博士学位,同年进入中国矿业大学工作,2017年在奥克兰大学访学。主要从事新能源新材料研究工作。主持和参与国家重点研发计划项目、GF重点项目、国家自然基金重点项目/面上项目等,主持其它纵向项目近20项;完成企业委托项目40余项,使得企业增效数十亿元;发表SCI文章250余篇,发明专利70余项;获得省部级科技进步一等奖2项;主编专著2部;兼任中国化工学会理事、中国热处理学会理事、中国铸造学会理事、江苏省铸造学会副理事长、江苏省储能专委会秘书长等。

尹青
副教授/硕士生导师
中共党员,博士,副教授,硕士生导师。2021年毕业于北京化工大学,化工资源有效利用国家重点实验室,获工学博士学位,英国牛津大学无机化学系Recognized Phd student。主要从事无机二维层状材料的结构调控及电化学储能性能强化研究,包括阴离子电池,超级电容器,钠离子电池等。目前主持国家重点研发计划子课题、国家自然科学基金青年项目、江苏省自然科学基金青年项目、中国博士后科学基金面上等项目。在Adv. Funct. Mater、Advanced Energy Materials、Small、Chemical Engineering Journal等期刊上发表英文SCI论文40余篇。

赵丹阳
副教授/硕士生导师
中共党员,山东大学工学博士,副教授、硕士生导师,江苏省“双创博士”“科技副总”。2021年12月进入中国矿业大学材料与物理学院从事教学科研工作,主要从事先进电化学储能器件关键电极材料结构调控及电化学性能研究。目前主持国家自然科学基金青年基金1项,江苏省青年基金1项,已在Energy & Environmental Science、Advanced Functional Materials、Advanced Energy Materials、ACS Energy Letters、Nano Energy、Small等期刊发表SCI论文20余篇,获江苏省材料学会研究生教学成果奖特等奖1项,授权发明专利1项。
山海蓄能,共赴新程
高效储能团队期待怀揣能源梦想的青年加入,以创新之光照亮碳中和未来!
